In this guide we will learn about implementing HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT and DELETE using Jersey (JAX-RS). In theory these HTTP methods used for following purposes:
- GET: It represents one or a list of resources or sub resources.
- POST: It creates a new resource as represented by URI from the request payload.
- PUT: It change an existing resource as represented by URI from the request payload.
- DELETE: It delete an existing resource as represented by URI.
- HEAD: It has URI similar to GET, but server don’t send any response body. It used mainly to know response headers information.
We will create a small Employees Management HTTP API application with following features:
- Create new employee record (use POST with URI /employees)
- Get specific employee record (use GET with URI /employees/1234)
- Edit an existing employee record (use PUT with URI /employees/1234)
- List employee records (use GET with URI /employees)
- Delete employee record (use DELETE with URI /employees/1234)
We had tested or used following tools and technologies in this project:
- Jersey (v 2.21)
- Gradle Build System (v 2.7)
- Spring Boot (v 1.2.5)
- Java (v 1.8)
- Eclipse IDE
- Embeddable H2 database (v 1.4.x)
- JDBC
- SQL
Bonus: You will also know H2 database CRUD operations using Spring NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.
This is a part of Jersey (JAX-RS) Restful Web Services Development Guides series. Please read Jersey + Spring Boot getting started guide.
Gradle Build File
We are using Gradle for our build management (Using Maven rather than Gradle is very trivial task).
File: build.gradle
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = '1.2.6.RELEASE'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
classpath('io.spring.gradle:dependency-management-plugin:0.5.2.RELEASE')
}
}
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'spring-boot'
apply plugin: 'io.spring.dependency-management'
jar {
baseName = 'jersey-crud'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
}
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
targetCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jersey', 'com.h2database:h2:1.4.+'
testCompile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
eclipse {
classpath {
containers.remove('org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER')
containers 'org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER/org.eclipse.jdt.internal.debug.ui.launcher.StandardVMType/JavaSE-1.8'
}
}
task wrapper(type: Wrapper) {
gradleVersion = '2.7'
}
Tip: H2 database or any other embeddable database can automatically configured by Spring Boot with defaults if we have org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc or org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jpa dependency available. Spring Boot will auto configure H2 with following values (You can override these by making entry for it in application.properties or application.yml file):
spring.datasource.name= H2
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.datasource.initialize=true
spring.datasource.schema=schema.sql
spring.datasource.data=data.sql
Create Employee Entity
File: Employee.java
package in.geekmj.crud.domain;
import java.util.Date;
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Date createdOn;
private Date modifiedOn;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Date getCreatedOn() {
return createdOn;
}
public void setCreatedOn(Date createdOn) {
this.createdOn = createdOn;
}
public Date getModifiedOn() {
return modifiedOn;
}
public void setModifiedOn(Date modifiedOn) {
this.modifiedOn = modifiedOn;
}
}
We define an Employee Domain/Entity which used extensively in this program.
HTTP POST method
We are here defining POST method which will expect application/json payload converted automatically into Employee entity by Jersey and passed to method createEmployee for further processing.
File: EmployeeResource.java
package in.geekmj.crud.resource;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import in.geekmj.crud.domain.Employee;
@Path("/employees")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public class EmployeeResource {
private final NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public EmployeeResource(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate) {
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
}
@POST
public String createEmployee(final Employee employee) {
String sql = "insert into EMPLOYEE values(DEFAULT, :name, :address, :createdOn, :modifiedOn)";
SqlParameterSource namedParameters = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee);
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, namedParameters);
return "{'status': 'Record Added Successfully'}";
}
}
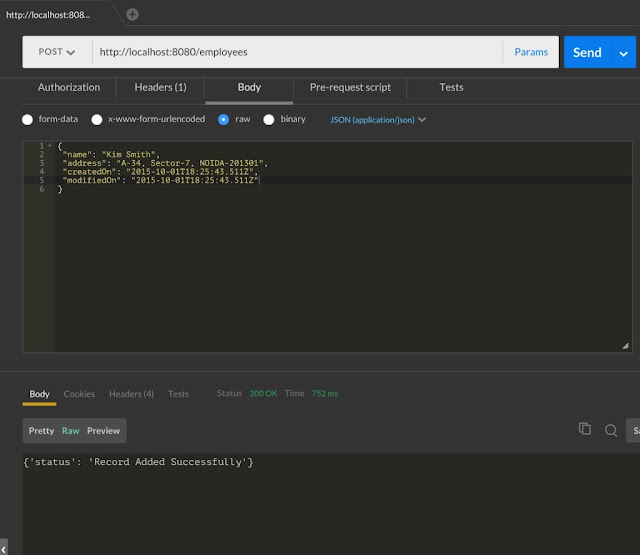
@POST demarcated method createEmployee is handling POST request at URI /employees for creating new Employee Record.
New Employee record inserted into embedded H2 database in memory using NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.update method.
Note: We optionally can give @Path at method level too.
You can execute Spring Boot application, as you run normal java program. Considering it is running.
We had sent HTTP POST request at https://localhost:8080/employees with employee JSON payload. See in above picture for more detail.
HTTP GET method
GET method to fetch a list of employee records.
File: EmployeeResource.java
package in.geekmj.crud.resource;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.DELETE;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import in.geekmj.crud.domain.Employee;
@Path("/employees")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public class EmployeeResource {
private final NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public EmployeeResource(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate) {
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
}
@GET
public List ListEmployees() {
String sql = "select * from EMPLOYEE";
return namedParameterJdbcTemplate.query(sql, new EmployeeMapper());
}
private static final class EmployeeMapper implements RowMapper {
public Employee mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
employee.setCreatedOn(rs.getDate("created_on"));
employee.setModifiedOn(rs.getDate("modified_on"));
return employee;
}
}
}
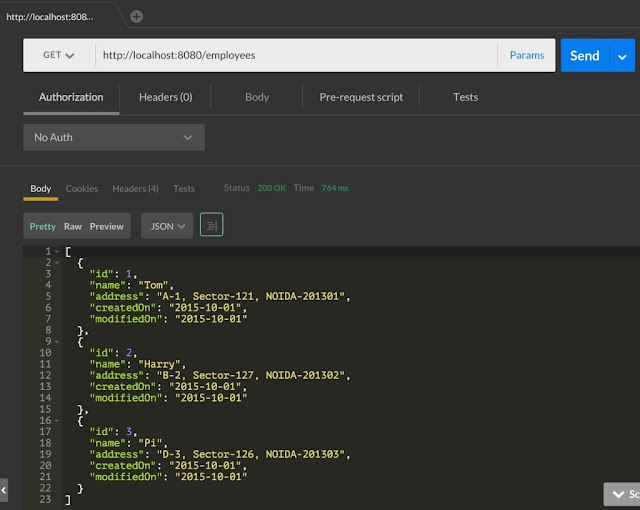
Employee records fetched from embedded H2 database using NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.query method.
@GET annotation used at method level to create HTTP GET method. We can test this API at /employees/ URI.
GET method to fetch specific employee record for id passed through path variable.
File: EmployeeResource.java
package in.geekmj.crud.resource;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import in.geekmj.crud.domain.Employee;
@Path("/employees")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public class EmployeeResource {
private final NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public EmployeeResource(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate) {
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
}
@GET
@Path("/{employeeId}")
public Employee getEmployee(@PathParam("employeeId") Integer employeeId) {
String sql = "select * from EMPLOYEE where id=:employeeId";
SqlParameterSource namedParameters = new MapSqlParameterSource("employeeId", employeeId);
return namedParameterJdbcTemplate.query(sql, namedParameters, new EmployeeMapper()).get(0);
}
private static final class EmployeeMapper implements RowMapper {
public Employee mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
employee.setCreatedOn(rs.getDate("created_on"));
employee.setModifiedOn(rs.getDate("modified_on"));
return employee;
}
}
}
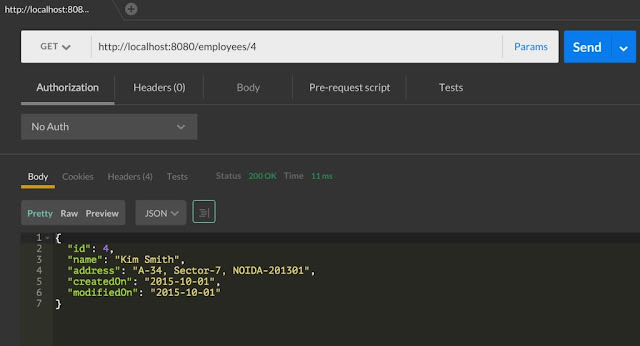
Specific Employee records fetched from embedded H2 database using NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.query method.
@Path has a path variable employeeId, when we will make GET request URI will look like /employees/{EMPLOYEE_ID}
HTTP PUT method
HTTP PUT method used for modifying an existing resource.
File: EmployeeResource.java
package in.geekmj.crud.resource;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.PUT;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import in.geekmj.crud.domain.Employee;
@Path("/employees")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public class EmployeeResource {
private final NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public EmployeeResource(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate) {
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
}
@PUT
@Path("/{employeeId}")
public Employee editEmployee(final Employee employee, @PathParam("employeeId") Integer employeeId) {
String sql = "update EMPLOYEE set name=:name, address=:address where id=:id";
SqlParameterSource namedParameters = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee);
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, namedParameters);
sql = "select * from EMPLOYEE where id=:employeeId";
SqlParameterSource namedParameters2 = new MapSqlParameterSource("employeeId", employeeId);
return namedParameterJdbcTemplate.query(sql, namedParameters2, new EmployeeMapper()).get(0);
}
private static final class EmployeeMapper implements RowMapper {
public Employee mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
employee.setCreatedOn(rs.getDate("created_on"));
employee.setModifiedOn(rs.getDate("modified_on"));
return employee;
}
}
}
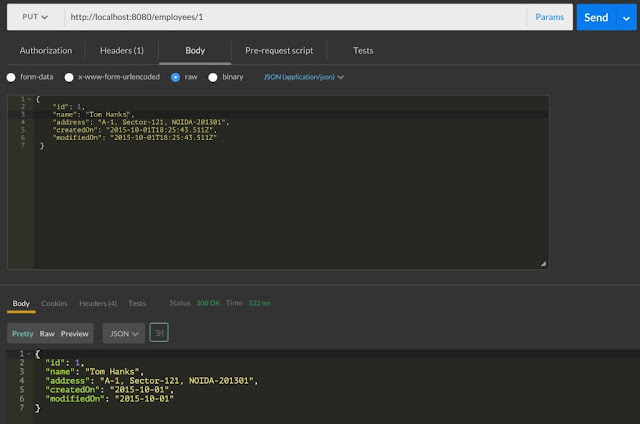
Employee records updated into embedded H2 database using NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.update method.
@PUT annotation used at method level to create HTTP PUT request handler which modify an existing resource. HTTP PUT method access at URI /employees/<employeeId>
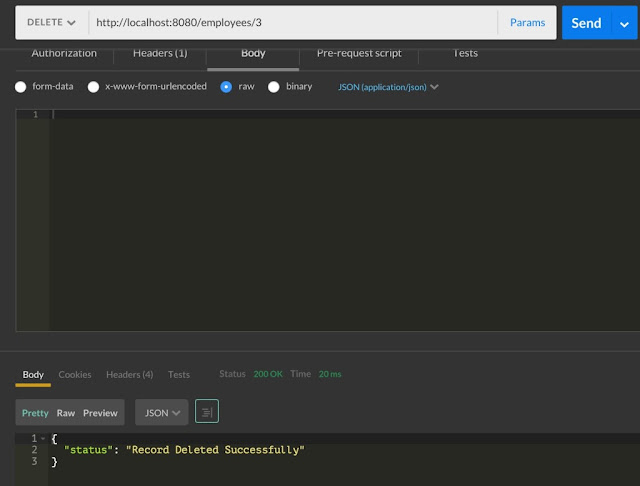
HTTP DELETE method
HTTP DELETE method used for deleting a resource.
package in.geekmj.crud.resource;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.DELETE;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
@Path("/employees")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public class EmployeeResource {
private final NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public EmployeeResource(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate) {
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
}
@DELETE
@Path("/{employeeId}")
public String deleteEmployees(@PathParam("employeeId") Integer employeeId) {
String sql = "delete from EMPLOYEE where id=:employeeId";
SqlParameterSource namedParameters = new MapSqlParameterSource("employeeId", employeeId);
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, namedParameters);
return "{"status": "Record Deleted Successfully"}";
}
}
Employee records deleted from embedded H2 database using NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.update method.
@DELETE annotation used at method to specify it is handling HTTP DELETE method. HTTP DELETE method used at /employees/ for deleting record with id passed using path variable employeeId.
References
- What is Request Payload?
- Official Jersey Documentation
- Download the Full Project
- Follow Project On Github